Send us your feedback
Here you can send us feedback on the Maxess-website. Please describe the problem or what’s missing in a clear way, and on what page you found the issue. Thank you so much for your help!


3D in situ analysis of the baking of gluten-free bread
Lyckeby, Sveriges Stärkelse-producenter, in collaboration with Garbo Food, wanted to investigate how different types of starches affect the time-dependent bubble formation that increases the volume of gluten free bread. To carry out the experiment, they chose to collaborate with RISE. Gluten-free breads often do not reach the same quality as their wheat-based counterparts. They often obtain less volume and age faster, which in turn can […]

A greener laser welding process
A collaboration of the laser specialist Trumpf, the Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology (ILT), the Chair of Laser Technology at RWTH Aachen and Hereon used X-ray videography at PETRA III to find a better for the Laser welding process of copper metal-ceramic welds in electrical vehicles.

A nano-scale glimpse into stainless steel brazing
Alfa Laval and Lund University used MAX IV to gain insights into the deoxidation process that occurs during the brazing of stainless steel products. These observations can help Alfa Laval to optimize its production process and solve R&D challenges. A leader in stainless steel products The Lund-based company Alfa Laval is an industry leader in the manufacturing of stainless steel products such as heat exchangers […]
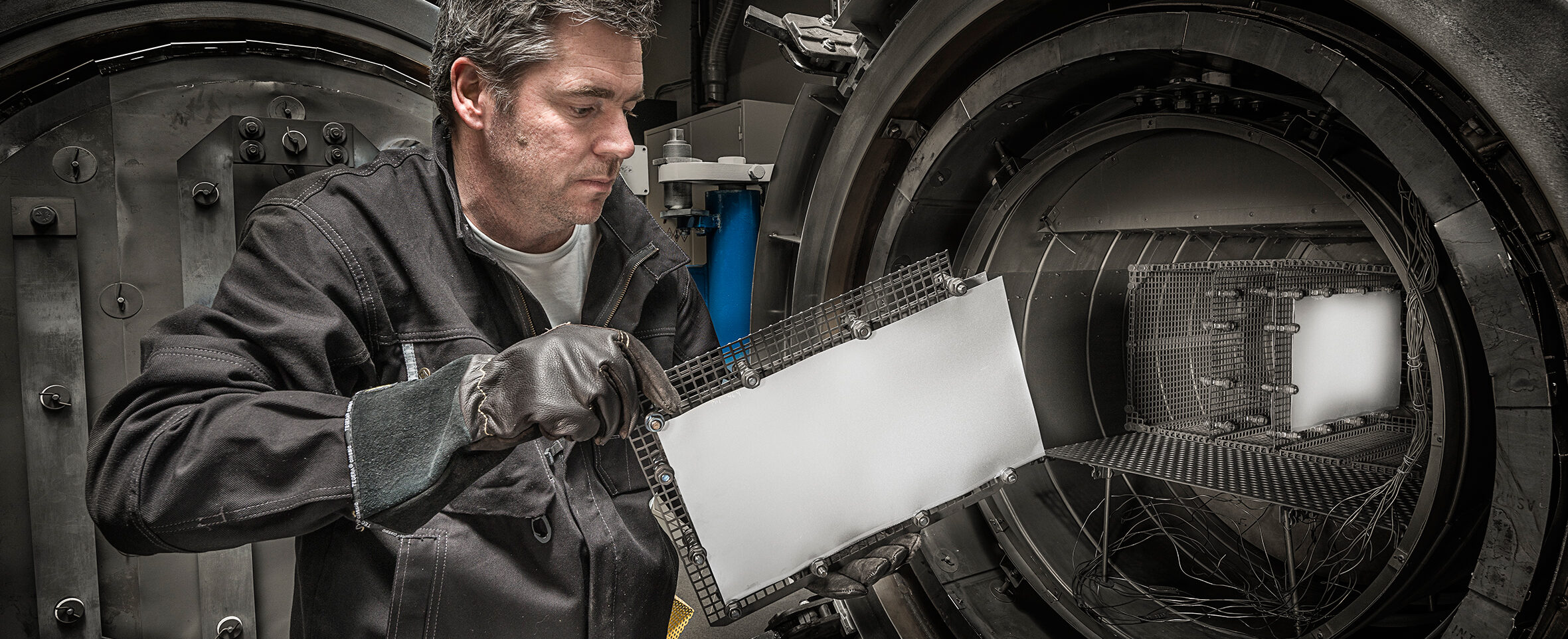

A push towards flux-free aluminium brazing
Gränges customers assemble aluminium sheets through brazing using braze clads, a fast and convenient assembly method. The technique used is called controlled atmosphere brazing, a procedure where brazing is performed in a furnace with nitrogen at temperatures around 600ºC. A crucial step preceding brazing is the removal of the surface oxide layer, which forms naturally on the aluminium surface.

A study of the freeze-drying process in probiotics
Freeze-drying is one of the most common ways to increase the shelf-life of probiotics and pharmaceutics. The Swedish probiotic company BioGaia wanted to follow the freeze-drying process in-situ to understand how the freezing, annealing and drying steps affect the final material structure. To do this they used large-scale infrastructure techniques. Freeze drying is a very established technique used in the pharmaceutical industry. The established protocols […]
An exploration of the micromechanical response of nitrocarburised steel
Volvo Trucks in collaboration with RISE wanted to study the micromechanical response of the joining zone of nitrocarburized steels. The project group, also consisting of Bodycote, KTH and Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon used insitu X-ray microdiffraction during nanoindentation. Synchrotron technique is unprecedented Every year, more than one million engine gears are produced at Volvo Trucks using nitrocarburizing heat treatment. This surface heat-treatment provides fatigue strength, corrosion protection […]

Better boxes for more sustainable packaging
BillerudKorsnäs together with RISE performed X-ray scattering experiments to understand the cause behind the deformation of corrugated boxes used in goods delivery. The collected data is contributing to the development of sturdier and more sustainable boxes. The way goods travel the world The use of corrugated boxes is the most common and wide-spread solution for the delivery of goods around the world, but it is […]

Bread at the nanoscale
Lantmännen and RISE want to establish new knowledge about the interaction of polysaccharides with water, and the gelatinisation of starch granules that shapes the baking process. The results of the X-ray scattering (SAXSSuitable for investigating the structure of partially ordered materials and systems, and characterising structures at various length scales and fast measurement times.More info) experiments help Lantmännen optimise the different qualities of their flours. […]
Can understanding potato starch aid in wound healing?
Malmö University together with Magle Chemoswed, investigated hydration of Microporous Polysaccharide Hemospheres, using SWAXS performed at MAX IV, combined with sorption calorimetry, gravimetrical swelling, rheology and differential scanning calorimetry experiments. The Microporous Polysaccharide Hemospheres are starch-based particles developed by the Swedish company Magle Chemoswed AB that can be used to accelerate wound healing.


Chemical Mill produces novel green fertilizer
X-ray experiments at DESY’s synchrotron light source PETRA III allowed scientists from the Ruđer Bošković Institute (IRB) , the Lehigh University in Bethlehem, the fertilizer company ICL, the University Zagreb and DESY to optimize a purely mechanical process for the production of Nitrogen and Calcium fertilizer.

Cleaner drinking water with neutron scattering techniques
Safe and readily available water is vital for public health, whether it is used for drinking, domestic use, food production, or recreational purposes. Sweden Water Research and ESS collaborated to explore how neutron scattering techniques can be used to develop more efficient water purification methods. Plastic use is ubiquitous in our modern-day society. Many plastic products contain the chemical bisphenol A (BPA), which is added […]

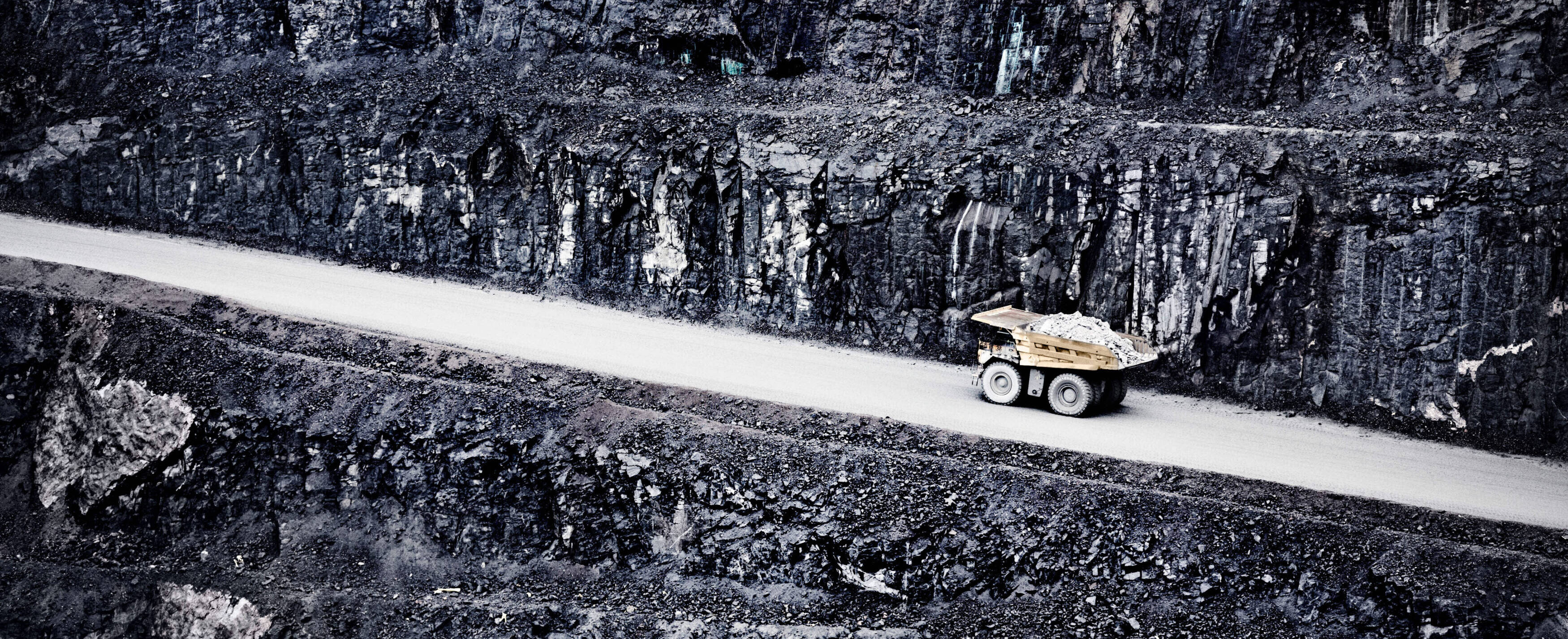
Cleaner steel with synchrotron X-ray microtomography
Steel producer SSAB, the metal research institute SWERIM and the Research Institutes of Sweden (RISE) used synchrotron X-ray microtomography to explore ways to detect foreign particles in predefined steel. The results show that it is possible to detect tiny inclusions down to a size of <2.4 μm.

Converting non-reactive biomass ash into environmentally friendly cement
Renotech Oy from Finland has developed a concept where biomass ash can be transformed into cement. Thermogravimetric analysis and synchrotron X-ray diffraction were combined to identify the best ash modification from their pilot biomass combustion unit.

Developing chemical-free cleaning with the help of synchrotron X-rays
Every year, billions of kilograms of detergents and cleaning agents are used globally, ending up in aquatic systems and accumulating in living organisms. To further develop a water filtration system without chemicals, SWATAB and Lund University used synchrotron X-rays at MAX IV.

Developing more durable concrete using neutron and X-ray tomography
To study what happens when concrete freezes, and is exposed to different types of moisture loads, Cementa AB, Malmö University, and Lund University have used neutron and X-ray tomography with the aim to develop concrete that is safer and more resistant to harsh weather conditions.
Developing novel peptide drug candidates using X-ray crystallography
Peptide therapy can be used to treat many diseases, including diabetes. The early-stage drug development company Follicum AB teamed up with SARomics Biostructures and Lund University using X-ray crystallography to explore new potential drug candidates based on tissue repair peptides.
Discover the true potential of your biomaterial with X-rays
BoneSupport AB and scientists from Lund University used X-ray tomography to observe how the bone substitute produced by the company behaves inside the bone. They confirmed the distinctive features of the product and observed how it protects the bone material during mechanical loading.

Enhanced cast iron for Scania’s vehicles
Scania together with Lund University and RISE used synchrotron light to gain deeper knowledge on how the cast iron elements used in their vehicles are subjected to stress that could lead to cracks. The gained knowledge is beneficial for both material R&D and product development activities, in the aim of developing improved cast iron components. The toll of heavy transports Scania is a world-leading provider […]

Finding drug candidates faster
SARomics Biostructures in collaboration with the BioMAX beamline’s scientists successfully tested the feasibility of serial crystallography at MAX IV. The advent of the first fourth-generation synchrotron pioneered by MAX IV finally makes serial crystallography more easily accessible to private companies. Crystals for drug development SARomics Biostructures is a contract research organization (CRO) offering structural biology services in the field of early-stage drug discovery. One of […]

Finding treatments for type 2 diabetes using X-ray crystallography
Diabetes is a chronic disease and a major cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke, and lower limb amputation. The drug discovery company Implexion Pharma and Lund University set out to explore new potential drug candidates for type 2 diabetes with the help of X-ray crystallography research techniques.

High speed X-ray radiography allows for the measurement of powder-based drugs inside nasal inhalers
The biopharmaceutical company Iconovo AB in Lund, Sweden together with MAX IV imaging experts carried out high speed Synchrotron X-ray radiography at the ID19 beamline at ESRF for studying the behaviour of powder-based drugs inside nasal inhalers. These experiments also confirmed that computational flow simulations of the behaviour of the powder-based drugs inside the nasal inhalers during intake were accurate.

How biological drug development benefits from photons
Alligator Bioscience in collaboration with SARomics Biostructures used X-ray crystallography to unveil the unique characteristics of one of their antibody-drug candidates, proving how valuable synchrotron X-rays can be for drug development. A promising antibody Alligator Bioscience, located just a few kilometres away from MAX IV, is a biotechnology company specialised in the development of antibody-based immunotherapies for cancer treatment. The company has a portfolio of […]

Identifying leaking syringes with neutrons
The biopharmaceutical company Sobi together with neutron experts from RISE used neutron radiography for the detection of leakages in prefilled syringes. The results show the potential of this technique in detecting leaks, with significant advantages for design and quality assurance in syringe production.

Identifying Toxic Compounds in Incineration Bottom Ash
Studying the speciation of zinc and copper compounds in thermal treatment residues to inform waste classification. Water Research Centre Limited (WRc) and DESY collaboration.

Improved packaging products using X-ray scattering techniques
Most polymer-based packaging opening devices are produced by injection moulding. The packaging company Tetra Pak and Chalmers University used small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS/WAXS) to learn more about injection moulding processes and improve the properties and composition of opening devices.

Improving laser powder-bed fusion processes using synchrotron X-rays
Laser-powder bed fusion is an advanced additive manufacturing technology for producing small and precise metal components. The gas company Linde and Chalmers University of Technology used synchrotron X-rays to study how to improve laser-powder bed fusion processes by looking at how helium influences the solidification of metal materials.

Improving metal cutting tools using X-rays
Metal machining is essential to produce components such as gears, bearings, clutches, tools, screws, and nuts. Seco Tools and Linköping University used X-ray absorption spectroscopy to acquire knowledge about tool wear behavior to develop more efficient cutting tools – and get faster production rates.

Increasing paperboard durability using neutron imaging
Cellulose-based paperboard is a renewable, recyclable, and durable packaging material. Scientists from the packaging provider company, BillerudKorsnäs, and researchers from Lund University have used neutron imaging to explore ways to make this material better resist water. Bridging knowledge gaps with neutron imaging Paperboard is one of our most widely used packaging materials for packaging food and beverage products, including juices, milk, and cereal. The packages are […]

Insights into better ways to package and deliver RNA into human cells
BioNTech, the biotech company that together with Pfizer developed one of the first COVID-19 vaccines, conducted scattering experiments at DESY’s synchrotron facility PETRA III in collaboration with the University of Mainz and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). Research questions and analyses were addressing the question how to better package mRNA in nanoparticles for vaccines or individualized drugs.
Investigating tablets
Magle Chemoswed explored the concentrations of polymorphs in with the help of X-ray powder diffraction both in lab-scale equipment and at DanMAX Beamline at MAX IV. The results where both interesting both for this specific active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and as a comparison between lab-equipment and MAX IVs capabilities. The experiment was made through guided access provided by MAXESS and SmiLe Incubator.

Looking inside a Battery
Together with the industry partner FINDEN LTD, DESY scientist used x-ray diffraction computer Tomography to gather insights into the inner life of simple AAA batteries to reveal their aging process and in order to make these last longer.

Mixing neutrons and photons for longer-lasting bread
Lantmännen together with RISE and Lund University combined neutron and X-rays experiments to look at the distribution of water inside doughs during proofing and baking. Their final aim is to produce baking products with a longer shelf life. Fresh for longer Wouldn’t it be nice if the bread you buy kept its freshly baked taste and texture for days? Wouldn’t it be convenient for resellers […]

More energy-efficient bread baking with synchrotron microtomography
Increased energy efficiency during bread baking can save time and energy, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and save money. Scientists from Finax and researchers from RISE and MAX IV used time-resolved synchrotron microtomography to explore ways to make bread baking more energy efficient.

New cancer drugs developed with the help of X-ray crystallography
Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020, or nearly one out of six deaths yearly. Scientists from the drug discovery company Sprint Bioscience and researchers from MAX IV used X-ray crystallography to take important steps toward developing new and more efficient cancer drugs.


Solving the crystal structure of novel complex materials
The company FAMAR conducted high resolution X-ray diffraction experiments for structural analysis of novel catalysts at the synchrotron facility PETRA III at DESY. With its new complex materials FAMAR aims to reduce C02 emissions in industry.

Stable emulsions under X-rays
Speximo AB and MAX IV Laboratory used the unique properties of synchrotron light combined with SAXS and WAXS techniques to obtain new information on the quinoa starches they use in Pickering emulsions. The findings are beneficial for Speximo’s future product development. Mixing oil and water Speximo AB is a Swedish company founded and run by experts in starch Pickering emulsions. The company develops oil-in-water emulsions […]

The road towards more stable biopharmaceuticals
The company Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB (Sobi) wants to know how to improve thermal stability of their biopharmaceutical products. Together with researchers from Malmö University, MAX IV, and RISE, they used synchrotron light to understand how proteins behave when water is removed from the pharmaceutical solution. Their findings can have important implications in the creation of more stable biological drugs. The challenge with residual water […]

X-ray scattering helps a global packaging company to optimize the polymer films
"How to make the production of packaging materials more sustainable?” is the subject that world-known company, Tetra Pak is interested in. To answer this question and engage in the thorough characterization of polymer films, the company turned to MAX IV laboratory.

X-rays can help stop wasting waste
Waste incineration companies working together with RISE investigated the use of synchrotron X-rays to identify nontoxic bottom ash from waste incineration that can be used as ground construction material. Bottom ash from waste incineration In Sweden, household and commercial waste that cannot be reused or recycled is incinerated, resulting in energy recovery and the generation of streams of fly ash and bottom ash as by-products. […]

XANES provided insights on mixing recycled material
Stone wool is an insulation material made from melted natural stone. The stone wool company Paroc AB wanted to gain deeper insights into how the iron in stone wool products can be affected by mixing recycled material containing a polyvalent element and chose to use X-ray absorption spectroscopy in collaboration with RISE and MAX IV. The popular insulation material stone wool is made from natural […]








