Send us your feedback
Here you can send us feedback on the Maxess-website. Please describe the problem or what’s missing in a clear way, and on what page you found the issue. Thank you so much for your help!
Developing novel peptide drug candidates using X-ray crystallography
Peptide therapy – targeted use of peptides to produce a specific reaction in the body – can be used to treat many diseases, including diabetes. The early-stage drug development company Follicum AB teamed up with SARomics Biostructures and Lund University using X-ray crystallography (MX) to explore new potential drug candidates based on tissue repair peptides.
Peptides are the building blocks of proteins. They occur naturally in the human body and are made from amino acids that are linked together. They bind to receptors on the cell surface and tell other cells and molecules what to do.
Understanding the binding and structure-function relationship of peptides to their receptor, in this case, pancreatic beta cells is essential for drug development processes and subsequent optimisation of drug candidates.
X-ray crystallography is the best-established method to investigate molecular interactions of drugs and receptors in high-resolution atomic detail. The research technique directly provides a 3D model that precisely traces peptide amino acid interactions, which is vital for understanding how the peptide binds to the receptor. Additionally, X-ray crystallography can reveal information about the peptide drug candidate and the complex protein with its receptor.
Therefore, the early-stage drug development company Follicum used X-ray crystallography to explore new potential drug candidates based on tissue repair peptides.
Investigating molecular interactions of drugs
A research team from Follicum, Lund University Diabetes Center (LUDC), and SARomics Biostructures performed the experiment at the I04 beamline at Diamond Light Source, UK.
Beforehand, binding parts of the receptor – pancreatic beta cells – and the target protein NRP1 were produced using cell cultures. The target protein, in complexes with different peptides, was purified and set up for crystallisation to produce well-diffracting crystals used in the experiment.
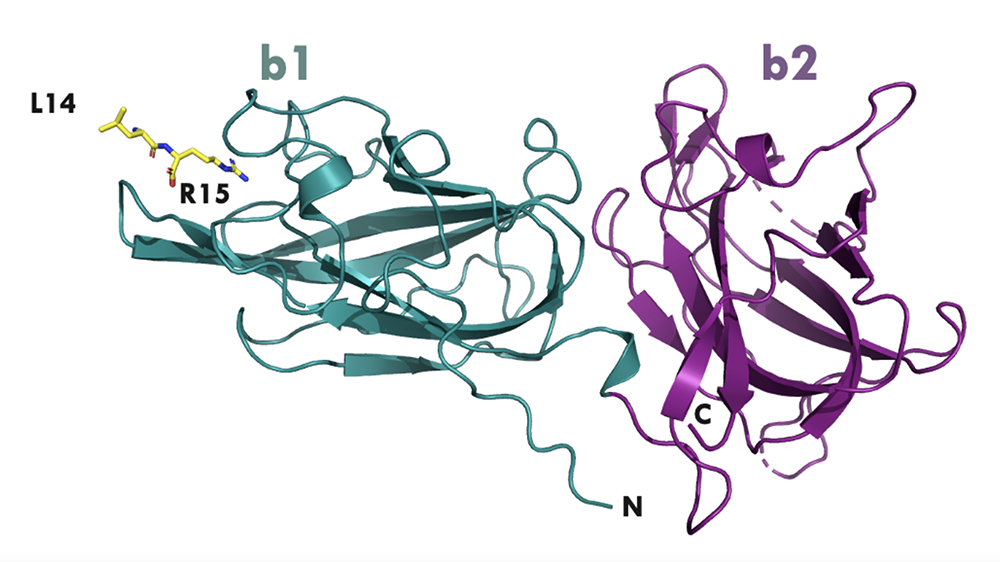
The data collected at the beamline made it possible to determine a high-resolution crystal structure of how the NRP protein in the complex with a peptide bound to the receptor. This binding has also been confirmed using traditional laboratory techniques at Lund University Diabetes Center using the purified NRP1 protein and commercially available NRP1.
The biological effect of the peptides was also evaluated. It confirmed their protective ability.
New knowledge will improve drug development processes
The collaboration provided critical structural insights into how the NRP1-peptide complex interacts with its receptor. The insights will enable an improved design of peptide structure and sequence.
Altogether, the research data and knowledge from the experiment have improved Follicum’s process for developing peptide platforms through rational peptide design.
“The collaboration using the synchrotron has resulted in an even better understanding of how one of our therapeutic peptide families affects important receptors on cells involved in tissue repair. This facilitates continued preclinical work and increases the opportunities to establish commercial cooperation with global pharmaceutical companies.”
Jan Alenfall, former CEO at Follicum AB
Contact Partners
Case Details
Follicum AB
SARomics Biostructures